Data backup gives us a sense of assurance that our data can come back to online no matter what happens to our system. Whether you are a backup administrator or a IT auditor, having a clear understating of the backup types will help you develop a strong backup strategy for your critical data and system files. This post aims to distinguish the difference between the major types of backups. At the end of reading this post you will be able to decide what types of backup suits you the best.
The three major types of backup are
- Full backup
- Incremental backup
- Differential backup
Full backup
A full backup takes backup of all the files regardless of whether they have been changed since the last full backup.
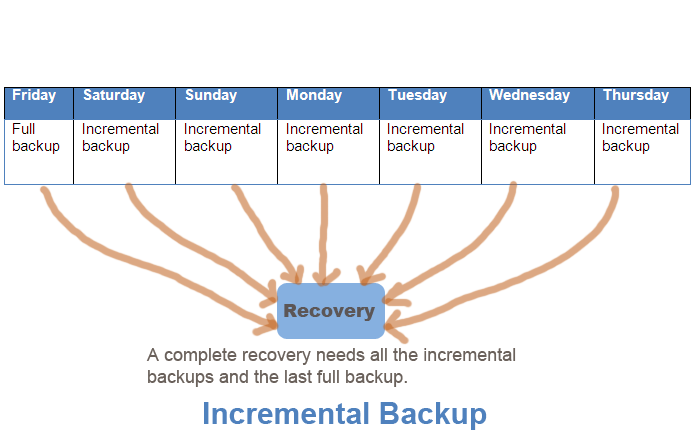
Incremental backup
This type of backup only backup the files that changed after taking the last backup. To store all the files to previous state, we need a full backup and all the incremental backups.
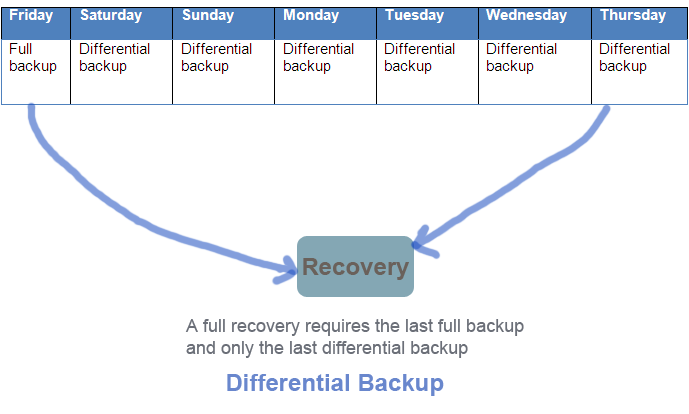
Differential backup
A differential backup means taking backup of all the changes that took place since the last full backup. This backup can be stored with a full backup and the last differential backup. Differential backup can be sub-divided into two -simple differential and multi-level differential backup. A multi-level differential backup is based on the same concept as simple differential backup except that it has nine levels. Any level of differential backup takes backup of files that has changed since the last full backup or the last lower level differential backup. For instance, if a full backup was most recent than a specific level of differential backup, then the level x differential backup will backup all files that has been modified since the last full backup, not the last taken differential backup.
Note: one important thing about backup is the status of archive bit. When archive bit is set to zero, it indicates that the files have been backed up, while an archive bit set to one means it has not been backed up. Remember that both incremental and full backup set the achieve bit to zero when the backup completes, which means when you take a full or incremental backup, your files will have archive bits set to zero. Only the differential backup keep the archive bit unchanged after taking a backup.
| Backup level | Advantage | Disadvantage |
| Full backup | Recovery requires just one single read form the backup storage device.No dependency between the two full backup. If one is lost you may use another recent full backup to recover certain amount of data, not everything. | The type of backup cause longest type of outage during the backup time.It is the most expensive type of backup because it takes maximum amount of storage space among all types of backup.
It also takes much longer time to run than its other counterparts. |
| incremental | Less media storage is required since it back up only the files that changed since the last backup.It take much less time in comparison to other types of backup. | Recover requires a full backup and all the incremental backup.A complete data recovery depends on the all the incremental backups and the last full backup. |
| differential | since differential backup takes backup of a series of changes since the last full backup, it requires less of number of backup sets to restore.They provide efficient recovery when full backup is taken rarely( e.g. monthly) | The amount of storage required for a differential backup may exceed than that is required for incremental backup when significant amount of data changes regularly. |
Which combinations of backup works best?.
It is recommended not to take all the three types of backup at the same time. Yu can take either full and incremental backup or a full and differential backup.
When you take both a full and differential backup, your back file size will be larger, but restoration takes less time. On the other hand, a full and a series of incremental backup takes less storage unit, but they need more time to restore than the combination of a full and differential backup.
When you choose the right types of backup to meet your needs, you need to be carefull about what to backup and what need to backup. Normally, many organization do not want to take backup of the operation system because they think that an OS can be installed in anyway. So, they do not care about the loss of system files. But, when if you have a highly customized operating system. Do you have enough time to apply all those settings that you applied over the years to fine tune the system. So, never undermine the benefits of taking backup of your operations system no matter which type of backup you are using.