DNS or domain name system is one of the most important parts of client-server model. Without a DNS no client could be part of a domain and there will be no way you can convert domain name into the IP address of the server. In this post you will find basic procedures that you can use to configure DNS for your domain controller. Though the procedures described in this post is applicable to Windows 2003 server environment, but it will help you to develop a good understanding to deploy and manage a DNS sever higher than Windows 2003 environment.
DNS installation procedures (forward lookup zone)
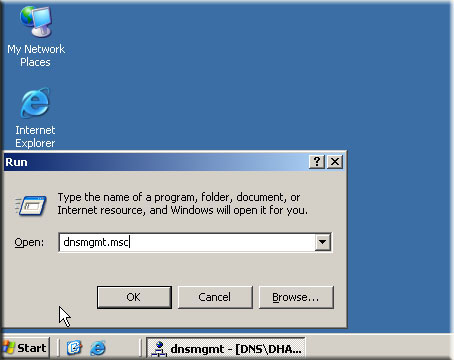
- In command prompt type dnsmgmt.msc
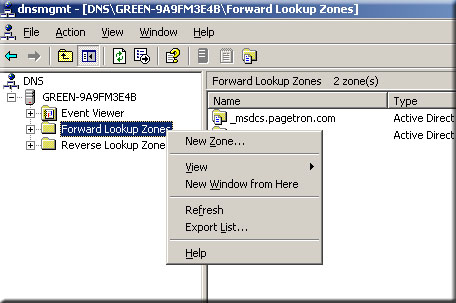
- Select forward look up zone and right click on it
- Select new zone and click Next.
- Select primary zone
- Store the zone in the active directory if DNS server is a domain controller.
- Name the zone (put the domain name)
- Select dynamic update
- Allow only secure domain.
- Next, finish.
- Right click on the domain name, select dynamic updates-secure only.
Create a reverse look up zone.
- Right click on the reverse lookup zone
- Select New Zone and click Next
- Select primary zone
- Select how you want your zone data to be replicated.
- Type the network ID of the domain
- Click Next and allow only secure dynamic updates
- Right click on the network ID under the reverse lookup zone
- Select new pointer and in the host name field type the server IP or browse the fully qualified domain name of your domain controller server.
- Right click on the computer name under the DNS and select all tasks and then select restart.
How to enable forwarder?
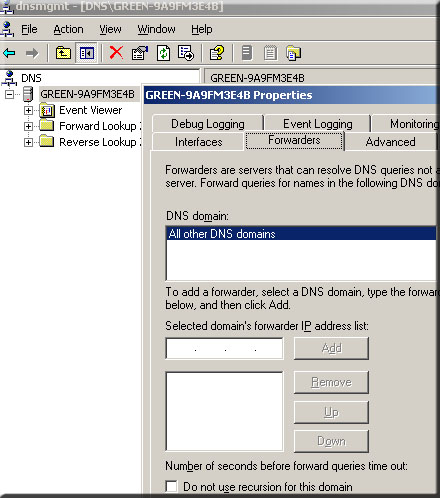
- Right click the server name
- Click on properties and then click on forwarder
- Type the IP address in the “selected domain forwarder IP address list”
- Click ADD and then OK.
How to add active directory integrated zone?
- Right click on the forward lookup zone
- Check the A.D.I.Z
Hot to copy of primary DNS/ How to configure secondary DNS server?
- Open you DNS
highlight forward lookup zone; right click on it. - Select new zone, click Next.
- Select secondary zone in the zone type
- Type a name for the zone and click Next. Zone name should be the same name as Primary zone.
- Master DNS server: set the primary DNS IP
- Click Add, next, OK
- Now highlight the reverse lookup zone.
- Right click and select new zone
- Select secondary zone
- Type network ID of the primary, click Next.
- Next write the IP of the server from which you want to copy the zone.
- Click ADD and Next.
- Now, right click on the domain name under the forward lookup zone.
- Right click and select properties.
- Select allow zone transfer
- Select only to the following server and type the name of
- The secondary DNS server.
- Highlight the reverser lookup zone and select properties.
- Select zone transfer and set the IP address of the secondary DNS server.
- Now, go to your secondary DNS zone.
- Select the forward lookup zone
- Put transfer from master.
How to set aging / scavenging?
- Open your DNS management prompt
- Right click on the server name
- Select Set aging and scavenging for all zones.
- Check “ set scavenge stale resource record”.
- Set no-refresh interval
- Server aging /scavenging confirmation
- Select apply these setting to the existing active directory integrated zones
- To manually check stale resource records, right click on the server name and then select “scavenge stale resource records”.
- To check DNS errors go to event view from the administrative tools and then select DNS server to find a list of errors.
How to manually add DNS client record/how to add static DNS record?
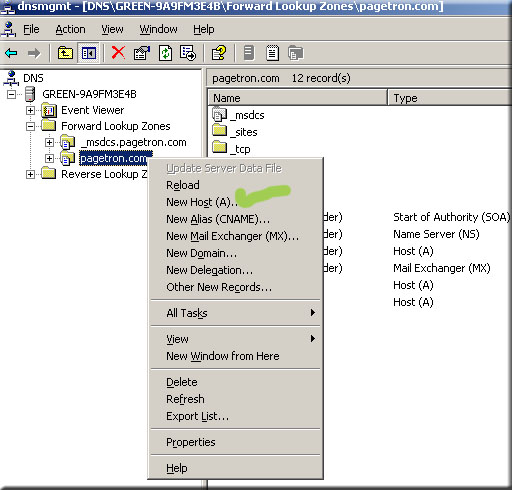
- Right click on the domain name under forward look up zone.
- Click on New host
- Type client name and IP address
- Select “create associated pointer PTR”.
- Click OK.
- Name aliasing
- Right click on the domain name of forward look up zone.
- Select new alias
- Give alias name
- Browse the computer name that will use the alias and click OK.
What is ageing and scavenging?
It is a parameter of DNS server to run garbage collection process to remove stale resource records.
DNS-WINS: the integration of DNS and WINS is the process to establish communication between WINS serer & DNS server client.
DNS event log:
It’s the monitoring process to figure out DNS server present status. For that we always have to check DNS service property.
NetBIOS name:
It’s a single PC name consist of up to 16 characters, where the 15 characters are used for name and the last or 16th character is used for identifying the services of the server.
Host name resolution process
When you ping the host name for example your host name is system05.security.com, your computer will first check the cache. If it does not find any answer, then it will check the host file. If host file fails to give any answer then the DNS server will resolve. When DNS fail to answer, the LM host file will try to solve the name. And finally WINS will resolve the name. In case WINS also fail to resolve the name then the domain name will be broadcasted. Remember that DNS maintains host file and the WINS maintains LM host file. Resolving name with the help of Host file and LM host file is known as static name resolution. The name resolution process used by DNS and WINS is known as dynamic name resolution.
What is recursive query?
Recursive query is a method where DNS server will take full responsibility for replying the client query.
What is forward lookup zone?
It converts domain name into IP address.
What is reverse lookup zone?
It is used to convert IP address to domain name.
List of DNS resource records:
- A – host record
- PTR- pointer to IP address
- NS- name server
- MX- mail exchange or mail server record
- www- web server
- CNAME- canonical name, alias record
Active directory integrated zone: if domain controller is made DNS then Active directory integrated zone and standard secondary will be implemented. If a member server is made DNS then it will get only standard secondary