VRRP or virtual router redundancy protocol provides router or switch interfaces failover and failback facility for seamless operation of a network. VRRP almost similar to HSRP in terms of operations and functions, but with a few added features such as VRRP supports up to 255 groups.
Just like HSRP, VRRP also support a number of routers to form a virtual group which acts like a single router. Every access request send to the virtual IP is responded regardless of the fact which router is in active mode. In VRRP only one router will remain active to forward all the traffic send to its Virtual IP address, and there will be one standby router and several candidate routers. In case of the active router failure or its interface failure, the role of active router will be shifted to the sandy router. And when the active router will be back in operation it will resume its responsibility as an active router.
VRRP Group-a group of routers participating in network redundancy with VRRP configured in them is called VRRP group, where there is only one router remains active, referred to as the master router, and one in standby mode and the other routers remain in the candidate list to become a standby in case of failure of the standby router.
VRRP characteristics:
- Switch with the highest priority will be the master switch. If you configure all the switches with the same priority value, then the switch with highest real IP becomes the master.
- Non-master switches will learn the timing from the master. To configure timers in non-master switch use the vrrp (group-number) timers learn command
- If you set the real IP as the vrrp id then the switch or router with that IP becomes the master of that group
- VRRP is a multivendor protocol, unlike HSRP which is Cisco proprietary protocol.
- VRRP can only track objects, not interfaces
When to use VRRP
If you already using HSRP for your network link redundancy then there are no direct benefits of changing over to HSRP. But if your network is mixed with both Cisco and non-Cisco devices then it is necessary to use VRRP, because HSRP only works with Cisco devices.
VRRP failover process
As you already know that VRRP provides dynamic failover facility. To ensure that dynamic failover, VRRP mainly uses three types of timers: advertisement interval, skew time and master down time. The advertisement time is the time which is expected by other routers in a VRRP group to receive message from the master router on multicast address 224.0.0.18 to inform that it is still active. When master router goes down, there is a specific time limit after which the standby router declares that their master is down. The default master down time is 3 x advertisement interval time+sket time. The skew time allows time for the standby router to become the new master.
VRRP configuration
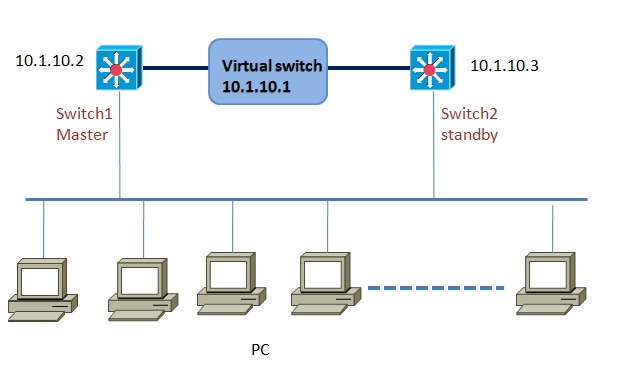
Let see how to configure VRRP in Cisco switches. Of course you can configure VRRP in routers, and there is little difference between configuring the redundancy between routers and switches. For configuring routers you need to assign VRRP commands in to interface and in switch you need to writer your commands under a VLAN. So, to configure VRRP in a switch you have to make a VLAN first and then assign an IP to that VLAN. Let assume that we have configured a VLAN called VLAN 10 and following the following commands
Swicth1(config)# track 80 interface fa0/1
Swicth1(config)#interface vlan 10
Swicth1(config-if)#ip address 10.1.10.2 255.255.255.0
Switch2(config-if)#no shutdown
Swicth1(config-if)#vrrp 1 10.1.10.1
Swicth1(config-if)#vrrp priority 110
Swicth1(config-if)#vrrp 1 timers advertise msec 500
Swicth1(config-if)#vrrp 1 authentication md5 keystring cisco123
Swicth1(config-if)#vrrp 1 track 80 decrement 20
The above are the most important and basic configuration a switch may need to join in a vrrp goup. After configuring switch 1, you need to enter switch 2 and assign a VLAN IP and the same vitual ip, timers, and audthentication key a as switch 1.Priority
Switch2(config)#track 70 interface fa0/2
Switch2(config)#interface vlan 20
Switch2(config-if)#ip address 10.1.10.3 255.0.0.0
Switch2(config-if)#vrrp 1 10.1.10.1
Switch2(config-if)#vrrp priority 95
Switch2(config-if)#vrrp 1 timers learn (since this one is not the master, it will learn the timer valued from its master)
Switch2(config-if)# vrrp 1 authentication md5 keystring cisco123
You do not have to configure track decrement command in this switch since this is the only standby switch.
More about VRRP configuration can be found in Cisco docs about VRRP.To learn about HSRP configuration take a look at HSRP configuration example