There are several types of firewalls that work on different layers of the OSI model. Depending on the kind of service and security you need for your network, you need to choose the right type of firewall. The following are the list of seven different types firewalls that are widely used for network security.
- Screened host firewalls
- Screened subnet firewalls
- Packet filter firewalls
- Stateful inspection firewalls
- Hybrid firewalls
- Proxy server firewalls
- Application level (gateway) firewalls
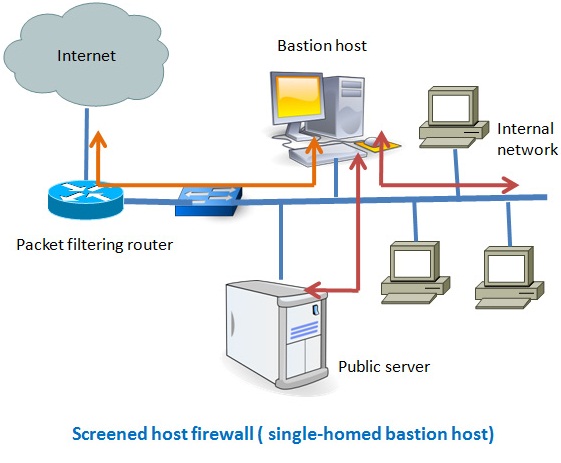
Screened host firewalls:
There are two types of screened host-one is single homed bastion host and the other one is dual homed bastion host. In case of single homed bastion host the firewall system consists of a packet filtering router and a bastion host. A bastion host is basically a single computer with high security configuration, which has the following characteristics:
- Traffic from the Internet can only reach the bastion host; they cannot reach the internal network.
- Traffic having the IP address of the bastion host can only go to the Internet. No traffic from the internal network can go to the Internet.
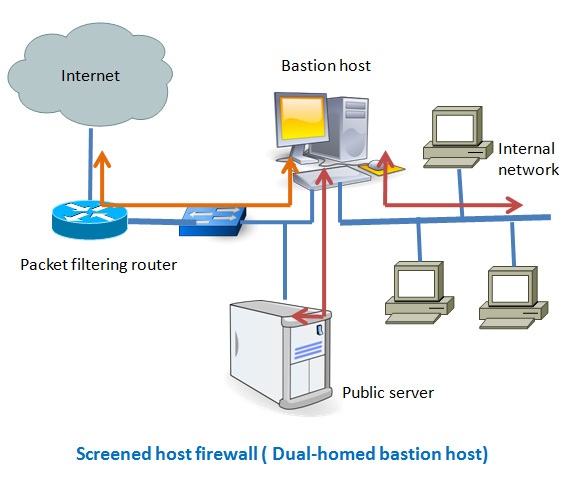
This type of configuration can have a web server placed in between the router and the bastion host in order to allow the public to access the server from the Internet. The main problem with the single homed bastion host is that if the packet filter route gets compromised then the entire network will be compromised. To eliminate this drawback we can use the dual homed bastion host firewall system, where a bastion host has two network cards- one is used for internal connection and the second one is used for connection with the router. In this case, even if, the router got compromised, the internal network will remain unaffected since it is in the separate network zone.
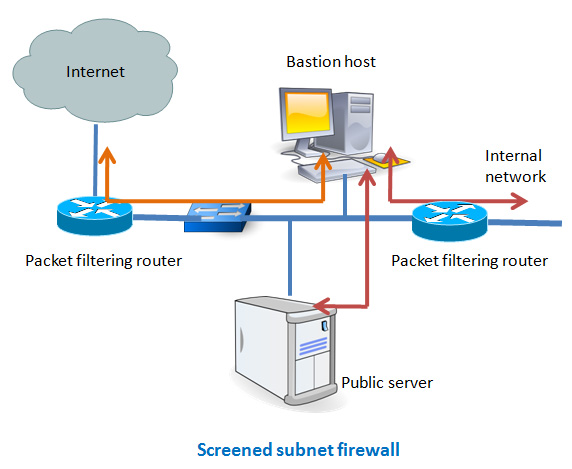
Screened subnet firewalls
This is one of the most secured firewall configurations. In this configuration, two packet filtering routers are used and the bastion host is positioned in between the two routers. In a typical case, both the Internet and the internal users have access to the screened subnet, but the traffic flow between the two subnets (one is from bastion host to the internal network and the other is the sub-network between the two routers) is blocked.
Packet filtering firewalls
This type of firewall is the most common and easy to deploy in a small-sized network. A router functions as a firewall by examining every packet passing through the network. Based on access control list, the router either forward or drop packets. Normally, the IP address of the source and destination, port number and type of traffic are taken into account when the router processes each data packet. Since a router cannot check packet in the application layer, this type of firewall cannot defend attacks that use application layers vulnerabilities. They also fail to fight against spoofing attacks. You can use this configuration if you need higher network speed and do need limited login and authentication capacity.
Stateful inspection
Stateful inspection firewall works at the network layer in the OSI model. It monitors both the header and contents of the traffic. The main difference between the packet filtering and the stateful inspection is that it the later one analyzes not only the packet headers but also inspects the state of the packets along with providing proxy services. Stateful inspection firewalls maintain a state table and a set of instructions to inspect each packet and store the information based on the type of traffic. It also monitors each TCP connection and remembers which ports are being used by that connection. If there is any port not required by the connection, then that port get closed.
Hybrid firewalls
They function almost the same way the stateful inspection type firewalls work, which means they can work both in network and in application level. Normally, in a hybrid system some hosts reside inside the firewall while the others reside outside of the firewall. To communicate with the machine outside the central network IPsec tunnels are used. An example where this type of configuration is suitable is a major site connected with its branch sites via VPN. One distinct feature of this configuration is the firewall administration at the major site distribute the security policy to its branch site so as a uniform security is maintained throughout the organization.
Proxy server firewalls
Proxy allows users to run specific service (FTP, TELNET, HTTP etc.) or type of connection by enforcing authentication, filtering and logging. For specific service there will be a specific proxy. For example, if you want to allow only HTTP connection to the Internet for your internal network users, then you must allow only HTTP proxy, nothing else. Users who need to go to Internet create a virtual circuit with the proxy server and the proxy server sends the request to connect to a specific site on behalf of that particular user. Proxy server changes the IP of the request so as the Internet or the outside world can see only the IP of the proxy server. Thus proxy server hides the internal network behind it. When a proxy receives the data from the Internet it sends the data back to its intended internal user via the virtual circuit. The main advantage of using proxy is that it is fully aware of the type of data it handles and can give protection to it. One disadvantage of proxy is that if there is an update of protocol that is used by the Internet, then the proxy software also needs to be updated to allow a specific service related to that protocol.