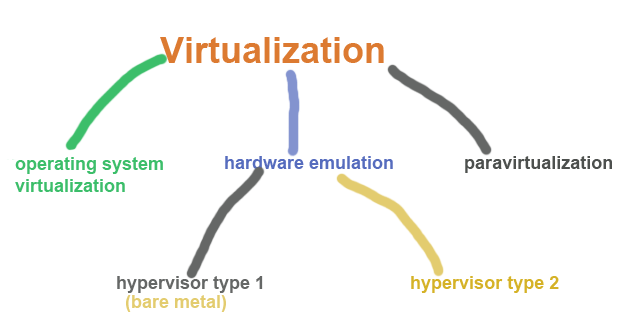
Virtualization helps to integrate several servers into a physical server in such a way that every server appears as a standalone server to the users. The three types of popular server virtualizations are OS virtualization, hardware emulation and paravirtualization.
Operating system virtualization
Operating system virtualization helps to create virtualized layer of software on the top of host operating system that resides above the hardware layer. Unlike other virtualization, they create an OS interfaces for applications to run, giving the feeling of a complete OS for the applications. Each virtualized environment has its own file system, system libraries, process tables and network configuration. Since they create a self-contained environment, they are also known as “container”. Therefore, creating the software emulation of an entire OS in a physical server is the essence of OS virtualization.
Disadvantage of OS virtualization
They support only one operating system as base and guest OS in a single server. You have to choose a single OS such as either Windows and Linux. All the OS in the container should be same version and should have same patch level of the base OS. If the base OS crash, all the virtual container become unavailable.
Advantages of OS virtualization
Since OS virtualization provide least overhead among all types of virtualization solution, they offer highest performance and highest density of virtual environment.
Application
They are great for isolating applications, web hosting and training. Popular OS virtualized products are OpenVZ and Virtuozzo.
Hardware emulator
In hardware emulation, a specialized software, which is also known as hypervisor, creates hardware emulation for OS in a single server. They can host different types of OS in a single server. The OS loaded into each virtual machine works as a standalone and unmodified OS. When a VM (virtual machine) is running, the hypervisor make changes to the part of the OS that make system calls. Hypervisor changes the OS by entering a piece of code—which is known as binary translation- to the OS when it is running. Binary translation takes place in four parts of the OS ( memory, processor, network, storage) that interact with the hardware.
Product: VMware utilizes hypervisor technology to their products.
Advantage
You do not have to modify the OS and applications to run on the virtual environment.
Types of hypervisor
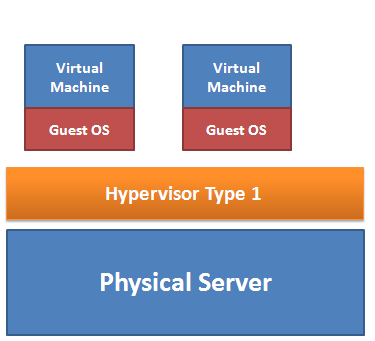
The two classes of hypervisor are: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 hypervisor is also known as bare-metal implementation because they sit directly on the top of hardware, without needing any operating system. Since they can directly communicate with hardware resources, they are much faster than type 2 hypervisor.
Advantage of type 1: if a single virtual machine crash, it does not affect the rest of the guest operation system. Therefore, they are considered more secure than type 2. Since they generate less overhead, type 1 hypervisor is much faster than its counterpart.
Type 1 Products: include VMware ESX, Microsoft Hyper-V, and the many Xen variants.
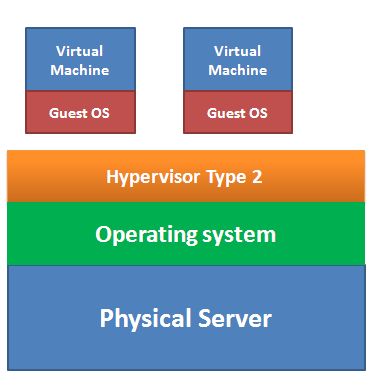
Type 2 hypervisor resides on top of the operating system. Since they cannot directly communicate with the hardware, they are less efficient than the type 1.
Advantage of type 2: in type 2 hypervisor, the OS takes care of all the hardware. That is why a type 2 hypervisor can support a wide range of hardware. Besides, installing a type 2 is much easier than that of type 1.
Disadvantage of type 2: they have more points of failure since anything that affect the stability of the base operating system can also affect the guest OS and the virtual machine. When the base OS needs a reboot, all the VM will also be rebooted.
Example of type 2 hypervisor VMware Player, VMware Workstation, and Microsoft Virtual Server .
Paravirtualization
Unlike hardware emulation, paravirtualization does not emulate hardware environment in software, instead it coordinates or multiplexes access to hardware resources in favor of virtual machine.
Example: Xen open source virtualization software.
In paravirtualized environment, a guest OS( called DomainU) is directly installed on the hypervisor(bare-metal architecture) that does not contain any device drivers for network and storage. Instead a privileged guest OS-also known as DomainO-has direct access to hardware. All guest OSes access hardware resources via DomainO). When a guest OS(virtual machine) needs to access hardware resources it sends a message to DomianO that access the hardware on behalf of guest OS. When data returns to the hardware, DomainO reads the information and passes it back to the guest operating system that has request it.
DomainO is a standard OS such as Linux that has been modified to communicate with hypervisor to control access to hardware.
Unlike hardware emulation, which has device drivers installed in the hypervisor, paravirtualization uses device drivers of the DomainO. All the guest operating systems have stub drivers that communicate with the stub drivers in the privileged guest. Instead of making direct contact with the hardware, each stub driver in the guest OS communicate with its counterpart in the DomainO. The main benefit of having stub driver is that the hypervisor does not have to have its own device drivers. Therefore, the users of the virtual machine never have to depend on the hypervisor software provider for driver software. Faster run time translation for system calls is the second benefit of this approach of device driver.
The major drawback of paravirtualization is the requirement of modifying guest operating system to execute and communicate with the hypervisor. You must modify the kernel of the guest OS before installation.
Since, it is not possible to modify the kernel of proprietary OS like Windows, paravirtualization software users ( such as Xen users) have to use open source OS like Linux or OpenSolaris.
| Virtualization type | Remarks | Products |
| Operating system virtualization | It creates an abstracted view of the OS including root file system, process table etc. They are suitable for homogeneous OS environment where consistent OS version is necessary. | OpenVZ, Virtuozzo, Sun Solaris |
| Hardware emulation | It Gives abstracted view of underlying hardware, offering support for heterogeneous OS.This is a market leading virtualization technology. | VMware VMserver, VMware ESX, Microsoft virtual server |
| paravirtualization | It multiplexes the access to hardware resources, offers high performance, requires guest OS modification before deployment.More complex than hardware emulation | Xen( open source) |
Application of virtualization
- For development and testing systems and applications
- Educational training
- Server consolidation
- Failover or high availability
- Server load balancing
- Server pooling
- Disaster recovery
Server consolidation means creating a union of physically separated servers. In the world of virtualization, consolidation means refers to taking several separate server instances and migrate them into a virtual machine running in a single server.
Having a clear understating on various types of virtualization technology helps IT professional to select the right virtualization solutions for the organization. So, before buying any virtualized products, you can consider testing open source virtual server solution such as Xen (though Xen commercial offerings known as Xen Citrix) that can give cost advantages to your business.