By following windows server security best practices, you can ensure that your server is running under the minimum required security settings. Implementing security best practices does not mean that your systems do not have any vulnerability. But, it gives a sense of security that your system will not be easily compromised and it least will perform better when it has to fight against well-known threats and risks. A list of frequently used Windows server security best practices has been given below. You do not require any special knowledge to implement the following settings.
- Patching systems– if you have less than 10 computers in your network, you may not need an automated patch management system. But patching Windows servers and desktop in a large network require a robust patch management system. An ideal patch management system will be able to automatically push a list of essential patches to the clients and servers, where the administrator will have complete control over on which security patch to be deployed. Besides, the patches must be tested in a test environment to make sure if the updates will cause any issue with the existing applications in the production environment.
- Antivirus solution- an antivirus solution is essential for networks of any size. When you are deploying antivirus solution, remember that it is configured for automatic update. An antivirus solution without updated virus signatures is useless.
- Log management- a system that needs to be fine-tuned for both performance and security need to have to log management system. Log management is all about generating the logs and reviewing it regularly. When setting up which types of information needs to be logged, you need to customize your setting to log only the crucial information that you need to monitor to assess your system’s performance and security issues. Too much logs can negatively impact the system.
- Disable unused services- it is a way to reduce the attack surface. An attack surface gets reduced when you expose fewer amounts of codes/services to the outside world.
- Delete unnecessary applications- this is another way to minimize the attack surface. The more application you have the more prone your system become to well-known vulnerabilities, leaving aside the possibility of zero-day-vulnerabilities. So, if you no longer use an application, simply delete it.
- Filtering ports- you need to be aware of the ports required by the services of you system. You certainly do not need running ports for FTP (20 and 21 TCP) or Telnet (23 TCP) in a computer that is used for Internet browsing or a server that is offering DNS service.
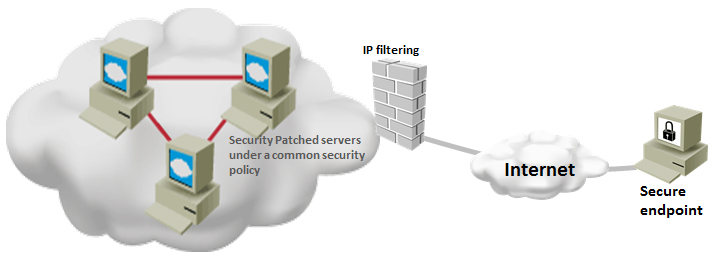
- Use IP filtering– if everybody does not need accessing your server, you can apply IP filtering to allow the IPs that only need accessing your server, denying all others.
- Custom scripts-if you are using custom script for taking backup or for sharing directory, make sure your scripts are not exposing.
- Delete default hidden shares/ unnecessary shares– if your server has any unnecessary shares, you can un-share it. If sharing a drive is necessary then make sure what kind of permission the normal users should have while accessing your shared folder. Do they have write access? If they have write access, you need to change it to read-only access.
- Physical and logical access control– make sure your server is physically secured and disable the USB port access as well as other external access to your server. Try to develop a policy for access control. Apply need based access policy so that only those who need to work on the server have appropriate access rights and permissions.
- Be careful of default permissions– checkout for the default permission of your drives and applications. If there are multiple privileged users accessing the server for maintenance work, you need to give them permission based on their needs. Do not give anyone privileged access if they do not require them.
- Use a host based intrusion detection and prevention system so that your system can automatically defend itself and take corrective actions without your intervention when it detects any unusual activity.
- Security assessment– you can use either open-source or commercial vulnerability assessment tools to assess the current states of you Windows servers.
- Use file integrity checker-If the system has sensitive data directory, you can use file integrity checker to investigate if anyone has tempered your data. You can run integrity check regularly, at least once in a week, based on your needs and the level of sensitivity of your data.
- Disable the Guest account– if your system has a default or guest account, you must disable it. Also, make sure all the applications installed on your server are not using default username and password.
- Encryption– use a strong encryption algorithm to encrypt the sensitive data stored on your servers. Also, make sure that the data on-the-move are also being transferred in encrypted format.
- Renaming default administrative account– this is the most basic thing that you need to pay attention to.
- Users with blank password– you must set passwords to all accounts that have no password. Make sure you have a password policy for each type user.
- Windows group policies– to enforce security settings on a large network; you can create a group policy template and apply it to your server in order to implement security policy efficiently.
- Emerging threats– the list of best practices described above are helpful to keep the Windows sever secure against well-known vulnerabilities. But you need to be vigilant about the emerging threats and the zero-day vulnerabilities. To protect your servers against the emerging threats you need to have somebody who can stay tuned with the latest threats and security breach trends.
Applying security policies and security settings are not enough to manage secure Windows environment. You need to assess the strength of your security regularly. Therefore, you need to have an audit plan where someone independent of your department can undertake an audit on your Windows machines. And finally, do not underestimate the power of developing security awareness program in your organizations so as your employees stay alert and help you detect any security breaches.
