From security perspective, not all types of data of an organization are equally important for successful business operation. Depending on business criticality, some data need to be more secured. The enormous computing power of cloud attracts businesses to put their data in the cloud, but many of the businesses do not have any decisive policy that defines which data to put in the cloud and what not to. This post highlights top 10 cloud security issues and risks that an organization needs to consider before migrating their mission critical data to the cloud.
What do you feel when you think about cloud security?Are you aware of the recent development of cloud security issues? Do you consult the data experts before putting your data in the cloud? Do you think that your data is more secured in a cloud in terms of data integrity and confidentiality?
Data is the core of any business, and most of the IT manager do not consider set aside a budget for data security unless there is a major data security breach in the organization.Remember that data is key element of a business.Therefore, when we talk about cloud security, we mean the security of data that is stored in the cloud.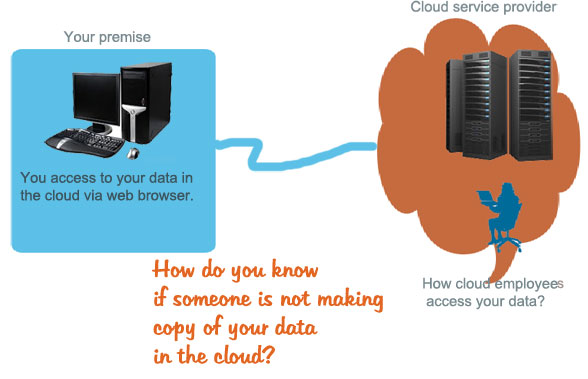
Remember that cloud security, primarily, depends on the types of cloud service and deployment models. The most popular types of cloud services are SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, and some widely-used cloud deployment models are public, private, hybrid, community. According cloud experts that private cloud is considered to be the most secure model for data.
- Lack of control on data: as soon as clients put the data on the cloud, the service provider takes control of data storage and its security. Clients have little control on how data is being handled in the cloud. Since all the data is processed in the cloud, there is always a risk of data theft and unauthorized access of data. Image a situation where you put your marketing data in the cloud and the service provider sells it to other marketing companies. Would you even know if your data is being stolen or used by your competitors? Besides, if you discontinue the service with your current service provider, there is a possibility that your data will still be stored in their cloud in multiple locations. How would you ensure that your data has been permanently deleted from all the data centres? So, before putting your data in the cloud consider how you plan to control your data access.
- Transborder: When data pass through the network from the cloud users to the data centres, it may pass through several countries that may access to the data and read it/make a copy of it. Unless you transmit your data in encrypted format, there is always a chance that someone can make a copy of your sensitive data.
- Data rights: since a cloud service provider may employ many vendors to handle data or can put data to other vendor’s cloud, it is extremely difficult to know who has what types of rights to the data.
- Vendor lock: there is always a possibility that you will not be able to switch to another cloud provider in case you want to move away from your current service provider. Cloud vendor lock happens because different cloud service providers use different type of virtualization software and the file formats, which need to be standardized so that clients can smoothly switch to the other cloud providers whenever they wish to.
- Location of data and regulation: according to EU council directive 95/46, your data can be transferred to outside of European country only when the country where you are migrating your data to gives you data protection adequately.
- Data segregation: since your data will share the same physical location with other clients, you need to ensure that your data is properly segregated. Most of the virtualization software can harden security of virtual instances (where your data resides in a server and behaves like as a standalone server). Therefore, secure your virtual instance to meet your security needs. Though it is a secure practice to avoid data co-location, it might increase your cost significantly.
- Data encryption mechanism: at first you need to identify what kind of encryption mechanism to use to protect your data. Do you think that encryption mechanise that you are using is strong enough and how your encryption keys are managed. Make plan to manage the security of your encryption keys. The types of authentication and authorization used to protect data are also a major security concern for cloud clients. Make sure that your cloud provider has the mechanism in place that can credibly prove to you that no data breach and unauthorized access has taken place.
- Data transmission: before you start using a cloud solution, you need to somehow move your data to the cloud. How do you transfer your data from your office to the cloud? How your cloud providers transfer your data when they send multiple copies of your data to different data centres? Make sure that your data is encrypted with strong encryption system while they are in-transit.
- Data backup: how your data is backed up? Is it stored offline? If so, what are the procedures and policies for the data backup?
- Prevent data leaking: how do you know that your data is not leaking from your cloud service providers. Make sure if the data prevention program of your service provider can prevent data leakage and what types of data leakage can be prevented (flash drive, FTP, email, applications etc.). A cloud provider may consider generating data leak prevention audit report and show it to its customers. Besides, a cloud user needs to know that the procedures used to grant privileged access to data.
Note: as you know that it is difficult to achieve security for an internal network. If it is so, then implementing and ensuring data security in a cloud, which is not located in your premise, is even harder. In a cloud environment, data do not reside on your premise, which does not necessarily mean that you do not have to be concerned about data privacy, identify and access management, physical security, incidence responses etc. In fact, the security issues are more complex in a cloud environment than an onsite environment.
Among all the cloud security risks, cloud data privacy seem to concern the cloud users the most since businesses always have the risk to lose its reputation and trust because of data leakage. If an organization fails to protect its own data, how its customers have confidence in them. Remember that IT also has an inherent threat of data leakage from its internal employees. Going for a cloud solution will always make your data expose to more risks. Therefore, before going for a cloud solutions, always think that what types of data you are going to store and process in the cloud, how those data are related to the critically of your business, and what level of risk you are willing to accept.
