A digital signature is an electronic equivalent of a physical signature. Just like the way a signature in a paper authenticates the signer, the digital signature also confirms the authenticity of the owner. Besides, it ensures that integrity of the data and non-repudiation. Non-repudiation means that the sender cannot later deny that he did not send the message. So, if you have a digitally signed copy of a document, you can say that the sender of the document is authentic and the data in the document has not been modified by any intruders. Therefore, a digital signature has three purposes:
- Authenticity of the source
- Data integrity
- Non-repudiation
Note: Remember that a digital signature never confirms the confidentiality of a document. Data confidentiality depends on the encryption mechanism.
Practical application of digital signature: for example, your customer regularly sends you order for product delivery via email. As you already know that receiving an email with a particular email address does not necessarily mean that the real person has sent you the email because emails address can easily be spoofed( a way to create forged sender address), which means that any intruder can send you a fake email using your customer’s email address. So, the question is how to confirm that the real customer is sending you the email, not any other person with evil intention. You will be sure about the origin of an email only when you are sure that the email is being signed digitally.
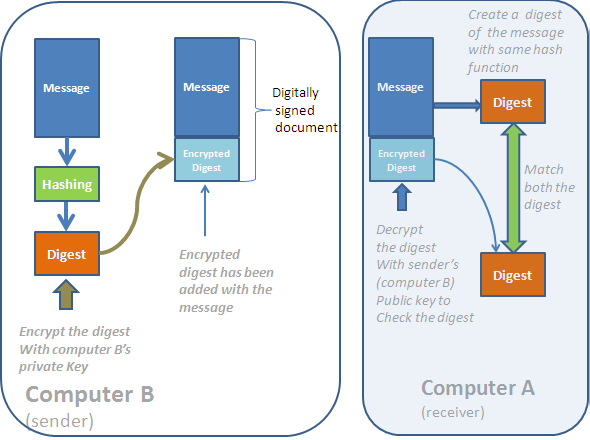
How digitally signed document is created?
For example, computer B wants to send an email or a digital document to you and you want it to be digitally signed so as you can confirm the source of the document. Before sending the documents to you, the computer B will follow the following process to create a digital signature:
- At first, computer B will create a message digest using contents of the document. Remember that a digest is a fixed-length string of characters that is created by applying mathematical equation(hashing functions) on the original message. So, every message has a unique digest and it will not match with the digest of any other message. After creating a digest, if anyone alter the original message and then create a digest, then the new digest will not match with the previous message. The digest will always be the same if only the message remains unaltered.
- Once you create a digest, you need to encrypt it with your private key. This encrypted format of the digest is called digital signature which is added to the original message and is sent to the destination.
- When the message arrives to its destination, the receiver will decrypt the digest using the public key of the sender. That will ensure the authenticity of the sender because the message was encrypted with the sender’s private key and it can only be decrypted with his public key.
- To prove the integrity of the message, the receiving computer will generate a digest from the message and match it with the received digest. If both the digest matches, it will ensure that the message was not altered by anyone on the way.
Components of digital signature
To sign a document digitally, we require two components: PKI (public key cryptography) and hashing algorithm.
Digital signature standard
In USA, NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) specifies the standard for digital signature which is known as Digital Signature Standard (DSS). According to this standard, all the federal office need to use SHA1 or SHA2 for hashing. This document also specifies the following three encryption algorithms that can be used in a digital signature:
- DSA-The Digital Signature Algorithm
- RSA-The Rivest, Shamir, Adleman
- ECDSA-The Elliptic Curve DSA
In simple words, a digital signature is a hash value that is encrypted with the private key of the sender and we use it to ensure data authenticity, integrity and non-repudiation.