One of the quickest and easiest ways to hardening your windows server 2008 r2 security is using automated tools to check the current security status of your server. Once you identify the security loopholes in the server, you can fix those security issues straight away. The good thing is that most of the tools can suggest a list of recommended settings that you need to use to fix the security drawbacks. The tools that you can use for securing Windows 2008 servers are:
- SCM ( Windows security compliance manager)
- MBSA (Microsoft baseline security analyzer)
- SCW ( Security configuration wizard)
Use Microsoft security compliance management toolkit (SCM)
This is one of the most comprehensive security compliance checking and deployment tools ever produced by Microsoft. The best thing is its free—you can download it at:
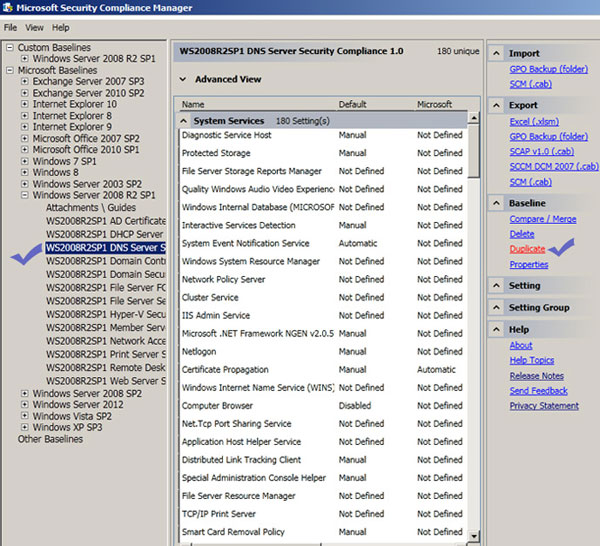
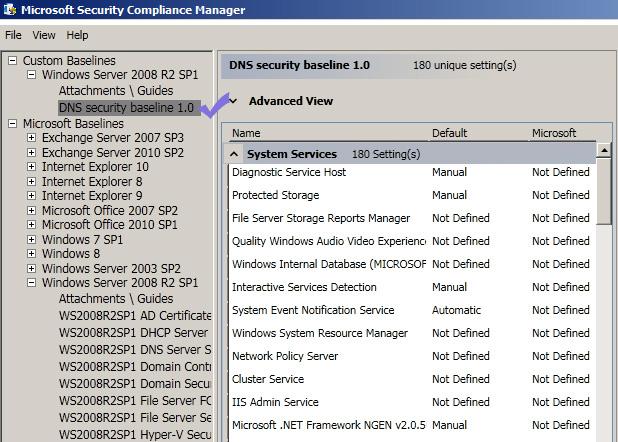
Once you download this tool, it will automatically update its security baselines for various Microsoft products such as Windows Servers, SQL servers, Internet explorer. Next, you need to select the product that you want to configure for managing your organization’s security compliance. For instance, windows server 2008 r2 has a number of security compliance for the services its runs such as IIS, domain controllers, active directory. You had better make a copy of this base line for customization. For example, you want to customize the security settings of your DNS hosted in a Windows 2008 r2 SP1 server. At first, click on the DNS under the windows server 2008 r2 SP1 and then click on “duplicate” on the right pane. The following screenshots illustrates what you need to do to make a copy of your existing DNS security settings. Next, type a name for that copy and then save it anywhere you want. Then, on the left pane you will see the copied baseline. You can customize it according to your security needs and export it.
Drawback of SCM:the main problem with new SCW 3.0 is the lack of useful documentation.
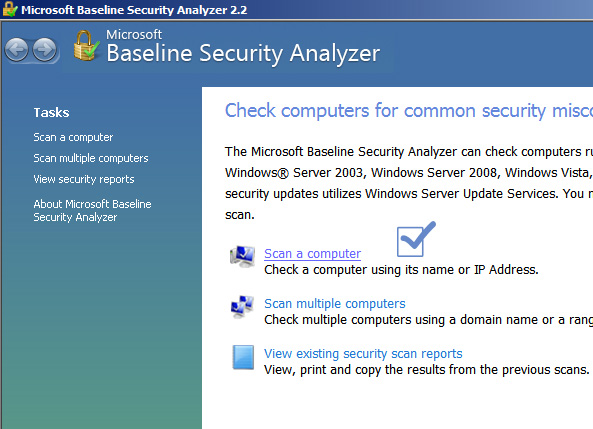
Microsoft baseline security analyzer (MBSA)
This simple tool can quickly identify that if your server has the latest updates or hotfixes. You can use it to install the missing security patches from Microsoft the keep your server align with Microsoft security recommendations. You can download this tool from Microsoft.
SCW (security configuration wizard)
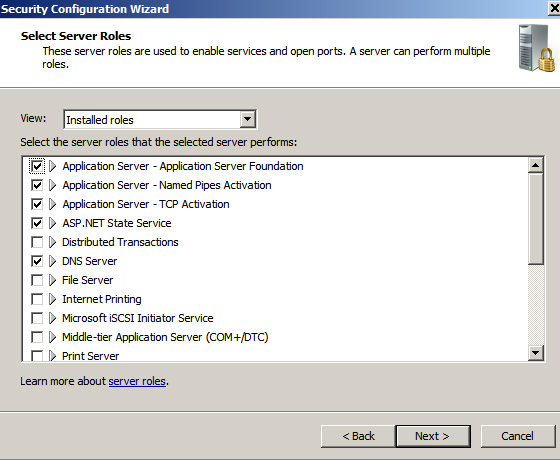
You can start SCW from the administrative tools from you Windows server. This is simply a great tool that can quickly identify the roles of your serves and the installed features including networking, Windows firewalls and registry settings. Based on the report, you can fine tune security settings for each feature such as network services, account settings, windows firewalls. At the end, you will be given an option to apply the settings to your server. If you choose to apply it later, then choose “apply later”, option and save it in your preferred location. When you need to apply the settings, you will need to run the SCW from the administrative panel, and then have to choose “apply an existing security policy” and browse the location you stored security settings.
You can check out the following video to see a demo on how to use SCW.
The next step is the manually check the following things:
Security settings of your server:
- Check for both local computers and domain security settings( if you server is domain member of domain controller).
- Check for user Account settings: both for local and domain users.
- Audit settings: configure audit settings to generate logs for the activities that you can consider might give you clues about the suspicious operation in your server.
Delete and Disable:
Unnecessary applications: delete all the unnecessary applications from your servers. For instance, you do not need to install Microsoft office applications in a web server because the purpose of a web server is to serve webpages efficiently.
Disable unnecessary ports with Windows Firewalls
Check your windows firewalls for the list of opened ports. Block all the ports that you do not need to run your applications. For instance, you may block the FTP ports if you never use FTP to upload and download files in your server.
Stop sharing folder or drive unnecessarily.
Check for the list of files or folders that you are sharing in the network. Do not forget to check for hidden shares.
The bottom line for Windows 2008 server security is:
Always remember to remove and disable anything that is not required.