Almost every Internet user has their home network that every family member use to Internet access.For your home network security you can follow a few simple steps to eliminate the chances of your network being compromised. Before diving deep into the home network security issues, you may have a look at the vulnerability points in your network, including your client machine.
The most vulnerable points of home networks are:
- Router security settings
- Security settings of Wi-Fi network
- Security of client machines/OS
Home router security
- Your home router is the access point to the Internet. A handful of free tools and techniques that can be used to break your network security have been discussed in the in this post.As a first step to secure your home network, you need to make sure you router is located in a physically secure location.
- Packet sniffers capture all data passing through the network. Though it is unlikely that anyone will install packet sniffer in your home network, there is a possibility that someone can tap your network, and use packet sniffer to capture the data packets. Look out for if there is any such device plugged into your network ports.
- Password crackers sniff data from the network. Usually a sniffer analyze the network data, just like the packet sniffer, and then brute-force to decipher the encrypted passwords.
- Network scanners are used to explore networks and host machines (server or client computer). Most of the home routers provide access-log that you can analyze to see to if there are any scanning type attack to your network. Normally, scanning is done only for reconnaissance purpose. You can run a network scan of your network to reveal which ports and services are vulnerable in your network. To tighten your network security, disable all the unused ports and services in your client machine.
- every router can be managed with remote access ports. Normally, vendors configure SSH (secure socket shell) in order to provide remote support to the customers. Talk to your Internet service provider to know if they are using any kind of remote access technique to remotely login to your router. If you discover that they have remote access, make sure they use some sort of encryption technique to access to your router.
Wi-Fi Sniffers
- Wireless sniffers identify wireless signals in the nearby area and extract data from it. So, no matter how your Wi-Fi router is secured, anyone outside of your house can still sniff wireless transmission, and extract the information from it. Therefore, make sure your Wi-Fi device is using a strong encryption method and keys.
Client machine security
- Keystroke loggers are small piece of software installed in a machine, which can record users’ keystrokes. Even if you use the strongest password of the world, the keyloggers can record it and send it to a specific destination machine. Always scan your machine to make sure if someone has installed key loggers to steal your sensitive information.
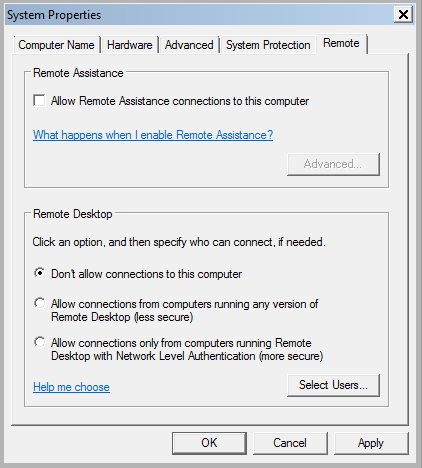
- Remote administration tools such as remote desktop, VNC can allow remote users to take control of your system. Many remote IT support company choose to use remote administrative tools to provide technical support to their customers. Make sure you allow remote access to your system only when you need it. If you are a Windows user disable remote assistance and remote desktop connection as shown below:
- Browser security: as you know that web browsers work as a gateway to the World Wide Web. Make sure your browser does not have unnecessary plugins and add-ons. Before installing any plugins, you can check if that plugin has any security issues. Turn off JavaScript, Java, Active X, which means client side mobile scripts need to be disabled if you don’t need them.
- Keep patching all your application software (Microsoft word, Adobe, PDF reader etc.)
- Run security updates of your operating system regularly. If possible update your OS.
- Never download and install unknown applications. Use only the application that has good security ratings. Before buying any application, research about its security history.
- Use a reputed Internet security solutions or antivirus scanner.
- Do not open unsolicited emails and avoid clicking links unless you know the sender. Remember that by clicking on a link you may allow a script to be installed surreptitiously in your computer.
- Learn about rootkits and use rootkit removal tools. Not all antivirus are smart enough in detecting rootkit.
- When you do not use your computer, disconnect it from the Internet.
- Pay attention to if your computer is running slower than before and look out for unusual behavior of you machine.
- Avoid downloading free software from unknown software. If you have to download a open source apps, then download it from the official site of the application.Remember that the attackers can infect any apps with malicious codes, and upload it to their website from free download.
- Do you have any network shared drive? If you are unsure about who have the rights to view your shared drives or files.If you do not understand how shared drive works, seek advice from some who knows.
- Beware of the cloud drive and its public share option. Do you have any publicly accessible folder in your cloud storage? Remember that if anyone uploads malicious program in your cloud drive, your own device might automatically copy that file from your cloud, which means your device is no longer secure.
To recap, turn off unnecessary services and ports that is not required and use a personal firewall or Internet security solutions in your network and beware of the inherent vulnerability of your operation system. No matter how many times you patch up your OS and applications, your system will always remain a target for zero-day vulnerabilities. Whenever you suspect that your computer has been compromised, disconnect it from the Internet by turning off Wi-Fi network interface or unplugging the network cable. Stay suspicious and informed.